 A database schema is an abstract design that represents storage of your data in a database. Learn the basics of database schemas with common examples.
A database schema is an abstract design that represents storage of your data in a database. Learn the basics of database schemas with common examples.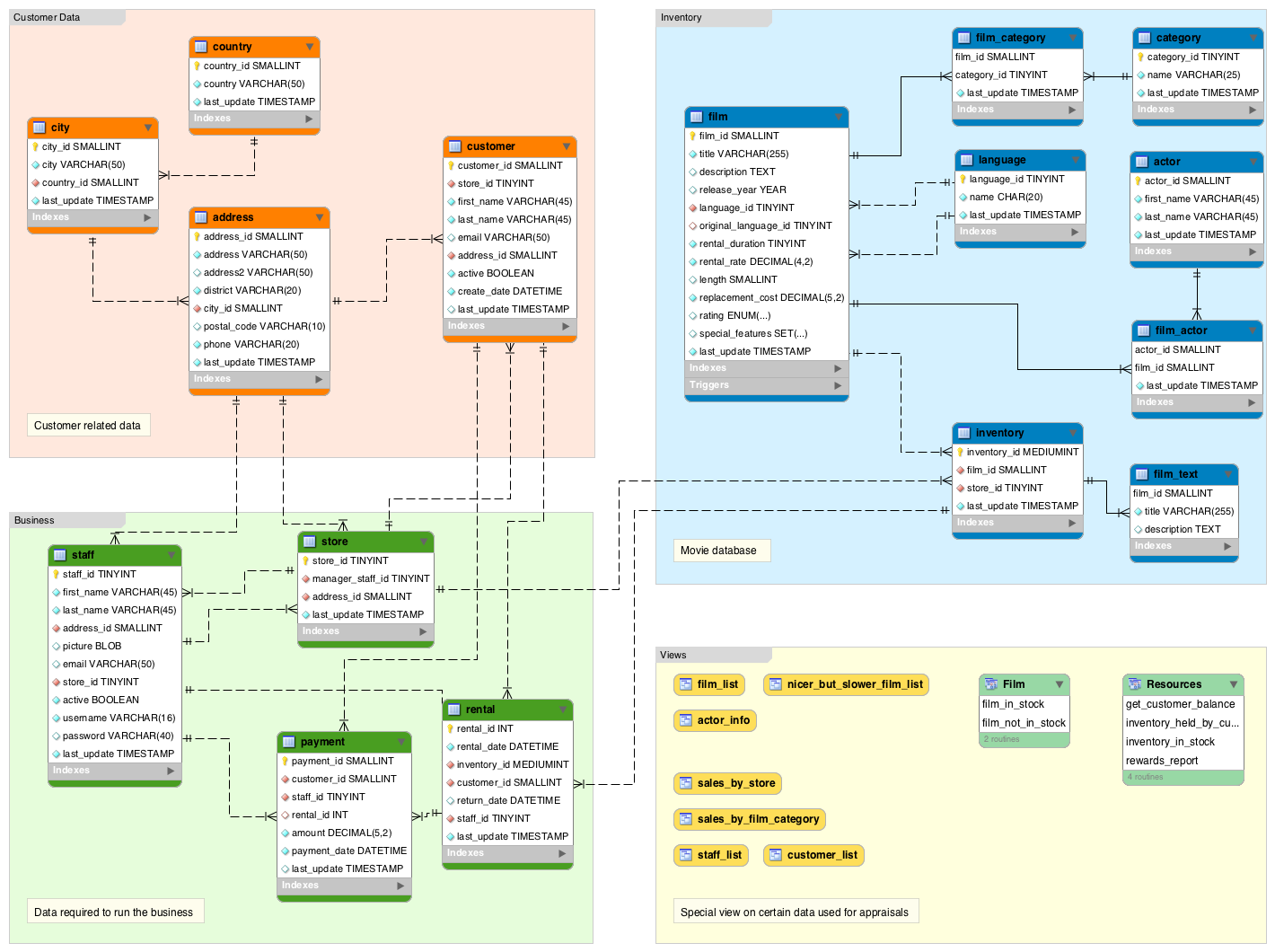 In database terms, a schema (pronounced “skee-muh” or “skee-mah”) is the organisation and structure of a database. Both schemas and schemata can be used as plural forms.
In database terms, a schema (pronounced “skee-muh” or “skee-mah”) is the organisation and structure of a database. Both schemas and schemata can be used as plural forms.